CT Computed Tomography
CT Computed Tomography
CT is a multislice spiral scan which allows the study of body sections with three-dimensional elaborations and generating 3D reconstructions.
We perform the following different body parts scan:
- skull: brain, skull base, ear, paranasal sinuses.
- head and neck: pharynx, larynx, salivary glands, orbit, paranasal sinuses, lymphnodes.
- thorax: lungs, pleura and organs of the mediastinum.
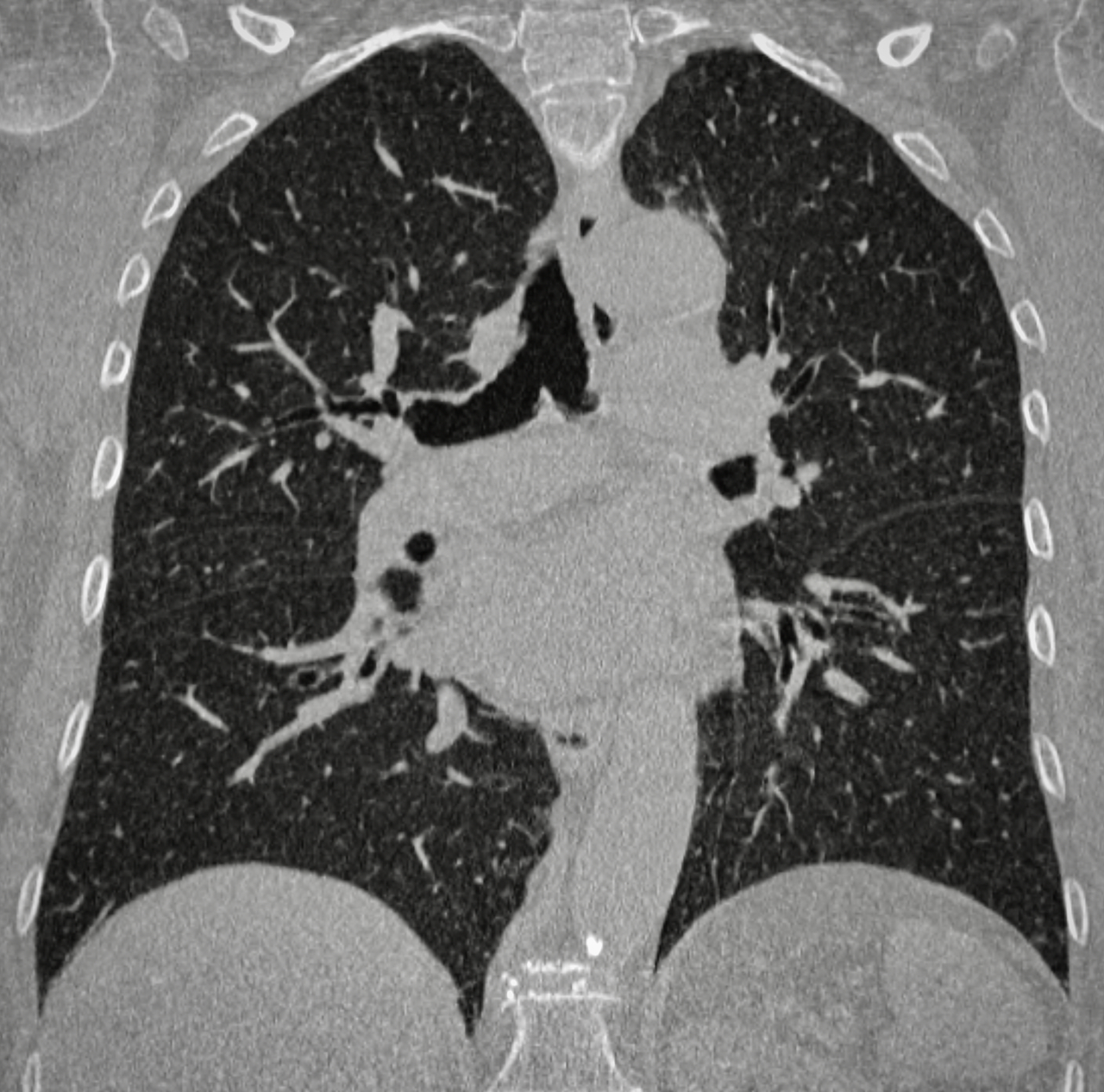
- chest with high-resolution technique (HRCT) for the study of the pulmonary interstitium.
- abdomen: liver, biliary tract, pancreas, adrenal glands, kidney, aorta and large abdominal vessels, retroperitoneum.
- male and female pelvis.
- musculoskeletal system: spine, pelvis, various joints.
Dentalscan
Some of the exams listed above, depending on the diagnosis, require the administration of intravenous contrast agent.
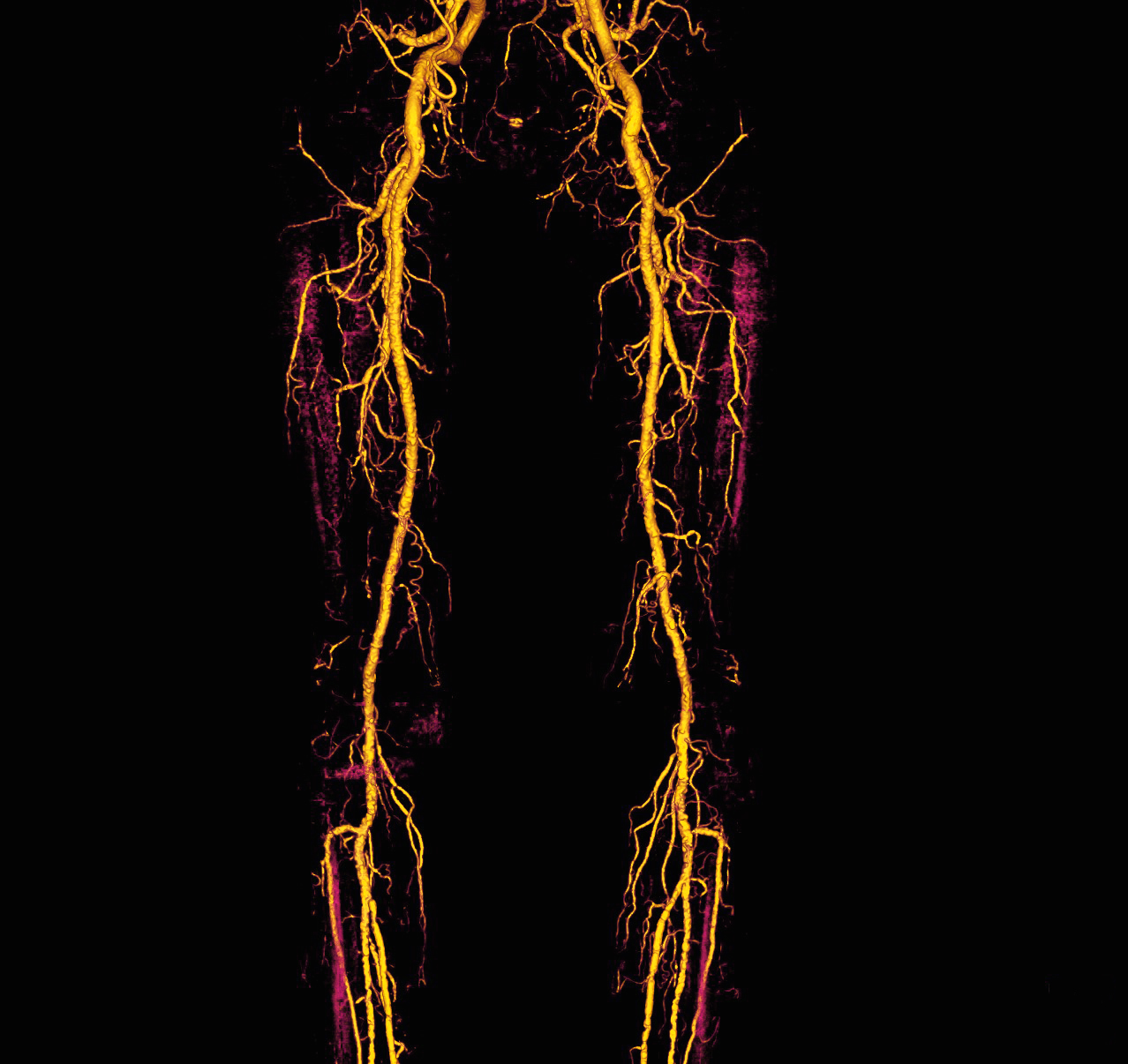
CT Angiography
The study of the vessels, especially arteries, with the CT scan method.
We scan the following vascular districts :
- intracranial arterial circulation.
- epiaortic vessels / supra-aortic trunks (SATs).
- aorta.
- abdominal arteries.
- arteries of the upper and lower limbs.
- pulmonary arteries.
The study always requires the use of the intravenous contrast agent.
The images can be processed by the radiologist with 3D electronic reconstructions such as volume rendering (VR), maximum intensity projection (MIP), multi planar reformation (MPR).
CT Colonography
It is a computerized tomography (CT) examination, performed at low dose after introducing air or carbon dioxide into the intestine via a small rectal probe using an automatic insufflator.
The images obtained from the two CT scans, performed in two different decubiti and lasting a few seconds, are processed on a computer with specialized software, producing two-dimensional and three-dimensional images including a 3D reconstruction of the intestinal mucosa in endoscopic vision.
The entire duration of the examination lasts a few minutes (about 10 minutes from the patient’s placement on the CT bed until the end of the exam), does not require sedation and, in order to screen for polyps or tumors, is performed low dosage and without contrast agent.
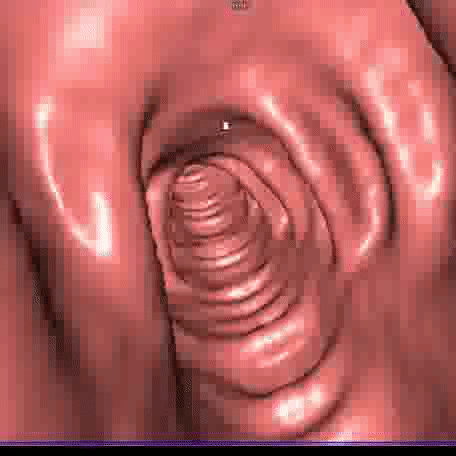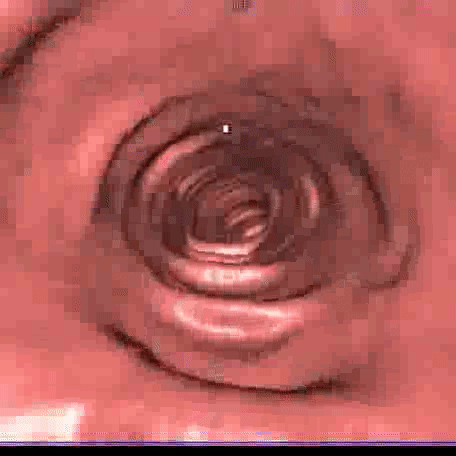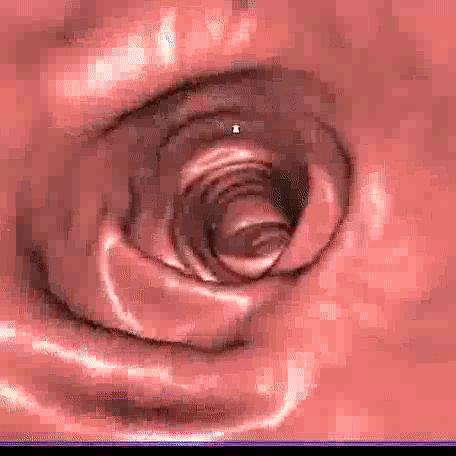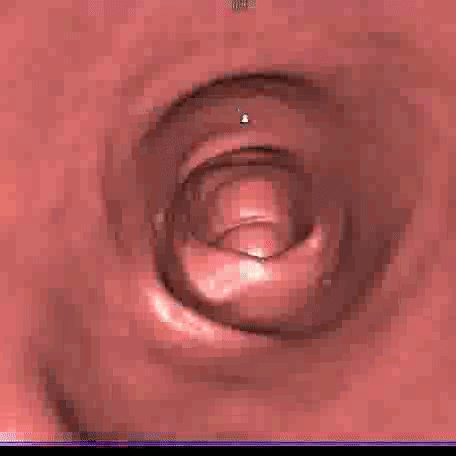
Indications for CT Colonography
What are the indications for performing a virtual colonoscopy?
Based on the evidence from scientific literature and the guidelines of the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) and the European Society of Gastrointestinal and Abdominal Radiology (ESGAR), virtual colonoscopy scans demand the following indications.
Absolute indications:
Previous execution of an incomplete or failed optical colonoscopy (causes eg: intestinal tortuosity, intolerance / pain, severe diverticulosis, obstructions due to masses, colonic spasms, …).
Elderly or frail patients (comorbidity, very advanced age, difficulty in performing optimal intestinal preparation essential for optical colonoscopy, anticoagulant therapies).
Study of diverticular disease and follow-up of diverticulitis (potentially risky with optical colonoscopy).
Symptomatic patients (gastrointestinal symptoms for colorectal cancer risk: bleeding, weight loss, pain, hypochromic anemia) who refuse optical colonoscopy.
Other indications: exact location of the tumor site established in colonoscopy before laparoscopic surgery, colon scan in patients with stoma, scan of known endometriosic lesions on the intestinal wall.
Prevention, as an individual choice instead of optical colonoscopy.
Relative indications:
II-level screening of colorectal cancer in patients with positive fecal occult blood test, or patients refusing optical colonoscopy as well as incompleteness and/or failure of the latter.
Surveillance of patients with colorectal cancer by associating an intravenous contrast medium administration to evaluate in a single follow-up examination (chest-abdomen CT) of both colonic and extracolonic findings (possible metastases).
Contraindications:
Acute abdominal diseases such as diverticulitis or acute inflammatory bowel disease (virtual colonoscopy can be performed two weeks after the resolution of the disease).
Recent endoscopic resection and recent biopsy (the CT Colonography can be performed two weeks later).
Long history of chronic inflammatory intestinal diseases (ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease).
Hereditary diseases such as Lynch’s syndrome or hereditary non-polyposis colon-rectal cancer (HNPCC), familial adenomatous polyposis (APC-associated polyposis).
Complications are very rare, the most fearsome is perforation (extremely rare compared to the traditional colonoscopy, generally it does not provide the need for surgery unlike those caused by the endoscope). Other possible and even more rare complications reported in literature, are vagal crises and angina.








